Ocular Psoriasis Treatment
Psoriasis-Ltd III is an ocular psoriasis treatment. Patients see an improvement in the appearance of their eye psoriasis within a few days. Use of Psoriasis-Ltd III will address the issues related to ocular psoriasis. The design of the Psoriasis-Ltd III disk allows for an easy application to the contour of the eye area. After washing the eye area with one of the two soaps recommended, leave the affected area wet and then glide the dry Psoriasis-Ltd III disk over the wet affected area for a 'quick touch' invisible application of the ingredients. The correct amount will be dissolved off onto the eyelid or other eye socket skin that is affected. Always apply the least amount as the next application may be 'just a little more'. OVer sensitive skin areas, 'Less is more' as a good standard measurement of application. The amount should always be invisible as the 'ingredients penetrate the skin and migrates to other areas.
A small amount of Omega-3's can make a big difference in the treatment of ocular psoriasis. A recommended dose of about 400 mg a day is required to help reduce ocular psoriasis symptoms. You can get it by consuming oil-rich fish such as salmon, herring, tuna, sardines, mackerel and trout. Other options would include 0mega-3 supplemental capsules on a daily basis.
Symptoms of Ocular Psoriasis
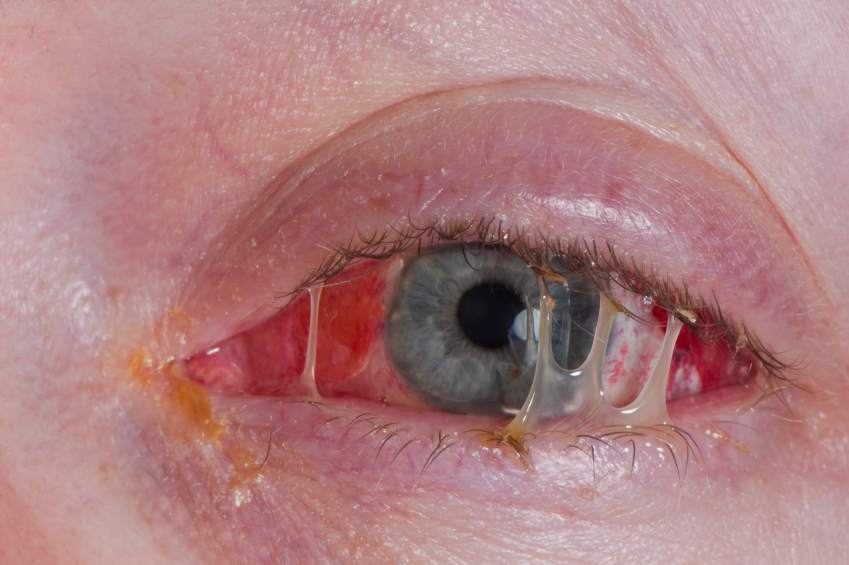
Ocular psoriasis can cause inflammation of the eye, dryness and discomfort. When psoriasis affects the eyelids, scales may cover lashes. The edges of the eyelids may become red and crusty. If inflamed for long periods, the rims of the lids may turn up or down. If the rim turns down, lashes can rub against the eyeball and cause irritation. In a prolonged ocular episode vision impairment may occur. Ocular symptoms may occur in approximately 10% of psoriasis patients. Ocular involvement is more common in men than in women. It is rare to have involvement of the eye prior to skin involvement of psoriasis.The ophthalmic signs of ocular psoriasis can vary widely, including Blepharitis, Conjunctivitis, Uveitis and Iritis. There have been reported cases of secondary corneal involvement resulting in keratitis.
Blepharitis is the most prevalent ocular occurrence in psoriasis. Erythema, edema, and psoriatic plaques may develop. Blepharitis is an irritation of the eyelids with irritation and inflammation or redness with swelling of the eyelids. Quite often the eye is dry due to extreme dehydration. A starting place for all is to consume much more water dependent upon your body size and humidity of the area that you live and the exercise and outdoor exposure. Remember to remove all mascara and make-up before going to bed.
Psoriasis can affect the eyes also
Ocular psoriatic conjunctivitis usually occurs in association with eyelid margin involvement of a psoriasis episode. Psoriatic plaques can extend from the lid onto the conjunctiva. Conjunctivitis, also known as pinkeye, is an inflammation of the conjunctiva, the thin, clear tissue that lies over the white part of the eye and lines the inside of the eyelid. Conjunctivitis is caused by viruses, bacteria, irritants such as shampoos, dirt, smoke, and pool chlorine, and allergies such as dust, pollen, or an allergy specific to those that wear contact lens. The symptoms of conjunctivitis differ based on the cause of the inflammation, but may include redness in the white of the eye or inner eyelid, increased amount of tears, a thick yellow discharge that crusts over the eyelashes, especially after sleep, green or white discharge from the eye, an itchy or burning sensation in the eyes, blurred vision and/or an increased sensitivity to light.
Uveitis and iritis frequently arise as a complication of psoriatic arthritis or lupus, in which the body's immune system attacks its own healthy tissue. Uveitis is an inflammation of the uvea, the middle layer of the eye's surface. The uvea includes the iris, the colored area at the front of the eye. When uveitis is localized at the front of the eye, it's called iritis. Iritis is redness and irritation of the iris. The patient will feel pain and very often a decrease in vision or blurry eyesight. Uveitis may affect only the fluid that fills the eye, but may also affect the small blood vessels behind the retina. Symptoms of uveitis can include: redness in the eye, sensitivity to light, blurred vision, pain in the eye or "floaters" in the field-of-vision. Early detection and treatment is of the utmost importance. Untreated uveitis can cause irreversible damage to the delicate eye tissue, and it represents the third most common cause of preventable blindness in the nation.
Keratitis sometimes occurs in ocular psoriasis. Keratitis can be very serious as there can be an infection of he cornea. Pain may result along with poor blurry vision with light sensitivity. You may wish to consult an eye specialist. Corneal involvement with ocular psoriasis is relatively rare. It usually occurs as a secondary to eyelid or conjunctival complications, such as dryness, trichiasis, or exposure.

